
MAB SLIM Series
Electromagnetic Brakes
The MAB SLIM is an ultra thin brake series designed for mobile robotics applications. Brakes are holding when power is off, providing high torque and low power consumption. The series is compatible with MAB MD Series motor controllers and has to be used with an overexcitation controller (included in the set). Brakes can operate in 24-60VDC power supply range and their modularity allows for choosing a holding torque from a wide range of 0.06-38 Nm.
How does an electromagnetic brake work?
Brake Released
Electric current flows through the coil generating a magnetic field which repels the armature, overcoming the spring force and allowing free movement.
Brake Locked
Mechanical springs pull the armature, creating a friction force which locks the brake and stops movement.
BRAKING WHEN THE POWER IS OFF
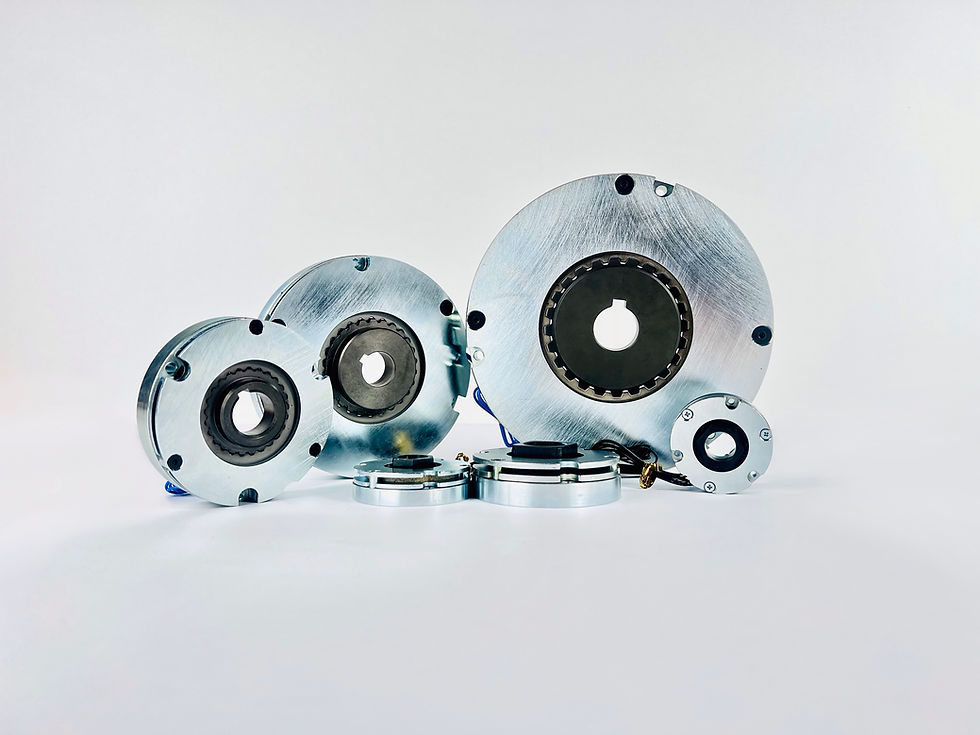

One of the key advantages of electromagnetic brakes is their ability to operate even without power. In the event of a power failure, relying solely on a BLDC motor for braking might pose a significant risk. Electromagnetic brakes act as a fail-safe mechanism, providing immediate and controlled stopping of the system regardless of whether power is available or not.
This feature can be critical in applications where safety is paramount, such as mobile robotics or industrial automation. The immediate cessation of motion in the event of power loss prevents the system from falling into an uncontrolled state, reducing potential risks and protecting both equipment and personnel.
BRAKING METHODS
While Brushless DC (BLDC) motors do possess inherent braking capabilities, they are primarily designed for smooth and controlled speed changes rather than precise stopping under high loads. The braking effect in a BLDC motor is typically achieved through regenerative braking, a process where the motor acts as a generator, converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy.
However, electromagnetic brakes offer a distinct advantage in applications where the braking process is required even in turned-off applications in contrast to BLDC motors which do not provide holding torque when a controller is disabled.

























